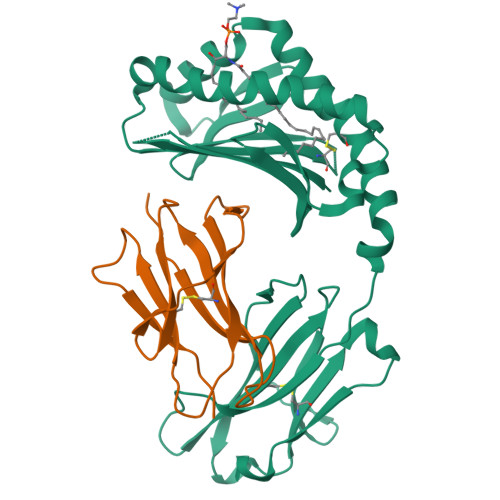
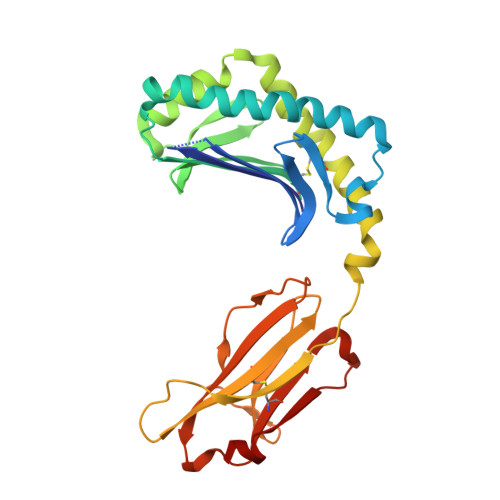
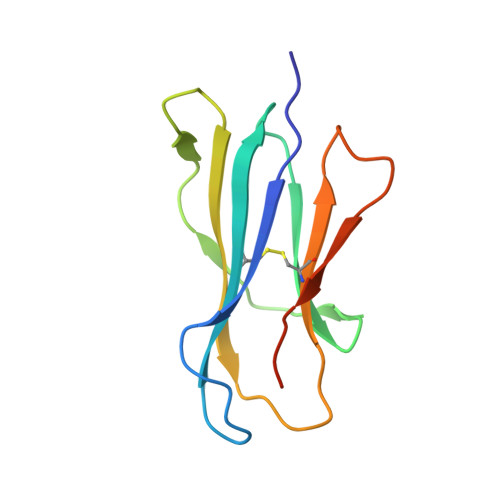
alpha beta T cell antigen receptor recognition of CD1a presenting self lipid ligands.
Birkinshaw, R.W., Pellicci, D.G., Cheng, T.Y., Keller, A.N., Sandoval-Romero, M., Gras, S., de Jong, A., Uldrich, A.P., Moody, D.B., Godfrey, D.I., Rossjohn, J.(2015) Nat Immunol 16: 258-266
- PubMed: 25642819
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3098
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4X6B, 4X6C, 4X6D, 4X6E, 4X6F - PubMed Abstract:
A central paradigm in αβ T cell-mediated immunity is the simultaneous co-recognition of antigens and antigen-presenting molecules by the αβ T cell antigen receptor (TCR). CD1a presents a broad repertoire of lipid-based antigens. We found that a prototypical autoreactive TCR bound CD1a when it was presenting a series of permissive endogenous ligands, while other lipid ligands were nonpermissive to TCR binding. The structures of two TCR-CD1a-lipid complexes showed that the TCR docked over the A' roof of CD1a in a manner that precluded direct contact with permissive ligands. Nonpermissive ligands indirectly inhibited TCR binding by disrupting the TCR-CD1a contact zone. The exclusive recognition of CD1a by the TCR represents a previously unknown mechanism whereby αβ T cells indirectly sense self antigens that are bound to an antigen-presenting molecule.
Organizational Affiliation:
1] Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Biomedical Sciences, Monash University, Clayton, Australia. [2] ARC Centre of Excellence in Advanced Molecular Imaging, Monash University, Clayton, Australia.